While both represent ownership in a company, they come with some distinct differences. When valuing common stock equity, there are two common models or techniques that can be used. The first is the constant-growth valuation model, also known as the Gordon Model. This model assumes that dividends will grow at a constant rate in perpetuity. In order to calculate the value using this model, we need to know the current dividend per share, the expected dividend growth rate, and the required rate of return.
Key Metrics for Common Stock Analysis
Traded on exchanges, common stock can be bought and sold by investors or traders, and common stockholders are entitled to dividends when the company’s board of directors declares them. Common stockholders can receive dividends, which are a portion of the company’s profits distributed to shareholders. However, unlike preferred stocks, dividends on common stocks are not guaranteed and can fluctuate based on the company’s earnings and decisions by its board of directors. The second common model for valuing common stock equity is the capital asset pricing model (CAPM). This model takes into account the risk of the investment and requires estimates of both the expected return and the risk-free rate. The CAPM is a more complex model than the Gordon Model, but it is generally considered to be more accurate.
How To Calculate Stockholders’ Equity
Any change in common stock will have an impact on the return of investors. When we decide to invest in one company, we lose the investing opportunity in other companies that may be able to generate higher return. Simply put, each share of common stock represents a share of ownership in a company. If a company does well or the value of its assets increases, common stock can go up in value. On the other hand, if a company is doing poorly, common stock can decrease in value.
- When investing in stocks, it’s essential to understand the differences between common stocks and preferred stocks.
- A stockholder owns 1% of the company if they possess 1,000 ordinary shares.
- If you invest in a diverse set of common stocks, you can spread your risk and reduce the impact of a poor-performing stock on your overall portfolio.
- But the question of whether they’re good for companies in the long term is more complicated.
What Are Dividends?
When a company buys back its own shares, that stock is accounted for as “treasury stock” on its balance sheet. Treasury stock is no longer outstanding — the company itself now owns it, not an investor or employee, but it has still been issued. Treasury shares continue to count as issued shares, but they are not considered to be outstanding and are thus not included in dividends or the calculation of earnings per share (EPS). Treasury shares can always be reissued back to stockholders for purchase when companies need to raise more capital. If a company doesn’t wish to hang on to the shares for future financing, it can choose to retire the shares.
If the common stock has a par value, then whenever a share of stock is issued the par value is recorded in a separate stockholders’ equity account in the general ledger. Any proceeds that exceed the par value are credited to another stockholders’ equity account. This required accounting (discussed later) means that you can determine the number of issued shares by dividing the balance in the par value account by the par value per share. Some companies choose to distribute some of the profits on their balance sheet to common stockholders in the form of dividends, and each common stockholder is entitled to a proportional share.
Corporate finance professionals, such as investment bankers, may use common stock prices on the exchange as an indicator of a company’s performance. Additionally, one aspect of investment banking is bringing private companies through the initial public offering (IPO) process, making the company public. Once the company is publicly traded, it will likely issue common stocks. The value of common stock can rise or fall based on the company’s performance and market conditions, offering investors the potential for capital gains as the stock price appreciates.
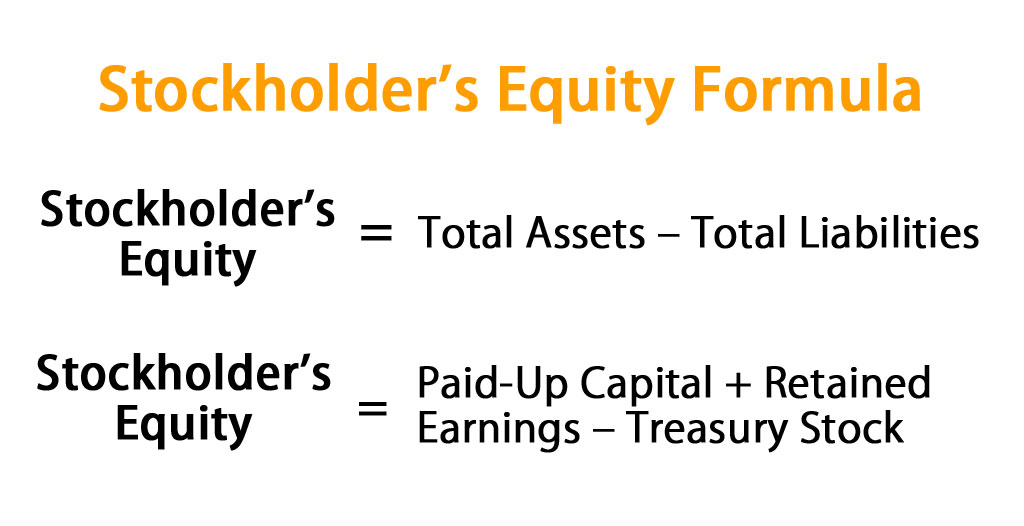
In addition, the CAPM can be used to estimate the cost of equity for publicly traded firms. However, like all valuation models, the CAPM has its limitations and should be used in conjunction with other information when making investment decisions. Stockholders’ equity is the remaining assets available to shareholders after all liabilities are paid. It is calculated either as a firm’s total assets less its total liabilities or alternatively as the sum of share capital and retained earnings less treasury shares.
Common stocks are represented in the stockholder equity section on a balance sheet. Now before knowing further about common stocks, have a look at a balance sheet. Common stock is a type of equity ownership in a company that gives the shareholder a share of the company’s profits and losses. Common stockholders usually have the right to vote and can take part in making business decisions. Understand the correlation between a company’s performance and its common stock value. Analyze financial reports and market trends to make informed calculations.
Businesses can choose whether or not and how much to pay in dividends to common stockholders. Preferred stock is a distinct class of stock that provides different rights compared revenue recognition with common stock. While both types confer ownership in a company, preferred stockholders have a higher claim to the company’s assets and dividends than common stockholders.
To keep track of each investor’s ownership interest, corporations use a unit of measurement referred to as a share (or share of stock). The number of shares that an investor owns is printed on the investor’s stock certificate or digital record. This information is also maintained in the corporate secretary’s records, which are separate from the corporation’s accounting records. A corporation’s accounting records are involved in stock transactions only when the corporation is the issuer, seller, or buyer of its own stock.
11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. Dividend is a reward, money, stocks which are distributed among the shareholders of that company. Dividends are decided by the board of directors and need the approval of shareholders. Examine the importance of historical data in predicting stock trends. Learn how past performance can offer valuable insights into future common stock movements.